How to Choose a Mortgage Type and Term
Learn how to choose a mortgage term and type that will save you money in the long run. Read on for our full guide to choosing a mortgage.
How to Choose a Mortgage Type - Adjustable vs Fixed
While mortgage lenders have come up with many creative ways to package their loans, they all still fall into these 3 basic types of mortgages: Fixed rate mortgage, adjustable rate mortgage and convertible mortgage.
Depending on the current market interest rates, choosing the right type of mortgage will heavily affect the overall cost of your mortgage loans.
Fixed rate mortgages are loans where the interest rates remain the same throughout the entire loan duration.
In times when prevailing interest rates are low (such as during a housing slump or economic recession), choosing a fixed rate mortgage is a clever way to lock in those cheap mortgage rates. A fixed mortgage rate also makes it much easier for you to estimate your future expenses.
To give you a better idea of the changing interest rates over the years, here is the mortgage rate chart from 1963 to 2012:
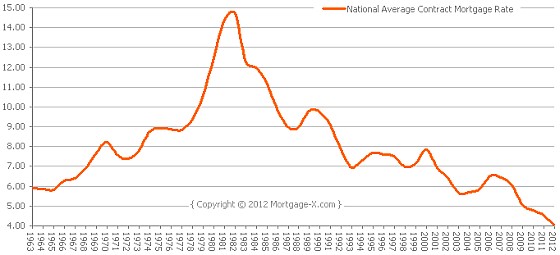
So when should you choose a mortgage with adjustable rates? ARM Adjustable Rate Mortgage (also known as floating rate mortgages) tend to be have lower interest rates for the first few years so this makes them more attractive to short term rental property investors - Just keep your eyes peeled for any ugly prepayment penalties that for switching mortgage lenders too soon.
To see the difference in interest rates between adjustable vs fixed rate mortgages, see our chart below (updated every month).
If you're paying for your mortgage with investment income that is dependent on market interest rates (such as stocks or bonds), ARMs also allow you to match your mortgage costs with your investment returns.
What if the market interest rates are sky high at the moment but you
have just spotted your dream home or profitable rental property? In that
case, you should consider choosing convertible mortgages instead.
For
this type of mortgage, your mortgage rates will vary according to the
market interest rates for the first few years (usually 3 to 7 years) and
you will have the choice to convert it into a fixed rate mortgage afterwards when the interest rates are lower and more affordable. The main attraction is that there are often minimal or no penalty fees for converting.
How to Choose a Mortgage Duration - 15 or 30 Years?
The length of your mortgage loan is something you must consider carefully as it will have a big impact on your mortgage rates and monthly mortgage payments.
In the past, almost all mortgages had the standard 30 year term. While 30 year mortgages are still common, borrowers today have a wider choice of loan durations to choose from: 10, 15, 20, 25 or even 40 years (15 years being another popular choice).
First let's talk about mortgage rates. When you choose a mortgage term that is longer (e.g. 30 years), your mortgage rates are going to be higher. The chart below shows the live interest rates of 30 year mortgages (in blue) vs 15 year mortgages (in orange):
A big advantage of longer mortgage term is having to pay less mortgage payments every month. However, the big catch is that a longer mortgage length also means you will end up paying more interest (vs someone who borrows the same amount at the same interest rate, but with a shorter term)
Let's illustrate this point with an example: Let's say that you want to take on a mortgage of $200,000 at 8% interest rate. What is the difference between a 15 year mortgage vs a 30 year mortgage?
Using our free mortgage payment calculator, you will find a 15 year mortgage has a monthly payment of $1,911.30 and you will end up paying the lender $344,034.75 in total. With a 30 year loan, your monthly mortgage payment drops to $1,467.53 but the total amount paid balloons to $528,310.49.
Just by shortening your mortgage period to 15 years, you will already enjoy a total savings of $184,275.64. And we haven't even factored in the reality that 15 year mortgages enjoy lower interest rates. However, it does come with a heavier monthly burden so make sure that your rental income (if any) plus personal earnings are able to cover it.
- How to Get a Rental Property Loan
- How to Choose a Mortgage Type and Term
- How to Finance Rental Property in 4 Steps
- Mortgage Application Documents Checklist
- Free Mortgage Payment Calculator
- 5 Proven Ways to Lower Mortgage Payments
- What are Mortgage Closing Costs?
- How to Lower Mortgage Closing Costs
- Introduction to Refinancing Rental Property
- 3 Top Reasons to Refinance Your Home


